So, what exactly is a variable speed drive (VSD)?
Think of it less like an on/off switch and more like the accelerator pedal for an industrial motor. Instead of just slamming the motor on or off, a VSD (often called a variable frequency drive, or VFD) gives you precise, granular control by adjusting the electrical frequency and voltage feeding the motor.
It’s the key to unlocking a whole new level of efficiency and control in modern industry.
Why VSDs are a Game-Changer
Picture this: you have a massive industrial fan, and your only control is a simple switch. It's either off or running at 100% power—no in-between. This all-or-nothing approach is incredibly wasteful and puts a ton of mechanical stress on your equipment every single time it lurches into action.
Now, imagine having that accelerator pedal. You can gently ramp up the speed, dial it in to the exact level needed for the job, and then smoothly ramp it down. That’s the power a VSD brings to the table.
For plant engineers, OEMs, and system integrators, a VSD isn't just another piece of hardware. It's a strategic tool for solving some of the biggest operational headaches. They are absolutely essential for:
- Dialing in Performance: VSDs let you match motor speed perfectly to the process demand, giving you unmatched control over applications like pumps, fans, and conveyors.
- Slashing Energy Costs: Why run a motor at full blast and then use a valve to choke the flow? It's like flooring the gas in your car while riding the brake. A VSD simply slows the motor down, resulting in massive energy savings.
- Making Equipment Last Longer: That jarring, across-the-line start is brutal on machinery. A VSD’s "soft start" capability eliminates that mechanical shock, reducing wear and tear on belts, gears, and bearings.
A VSD changes equipment speed to provide the torque-energy input needed to supply the hydraulic-energy output to the process. The most efficient means of flow manipulation is pump-speed adjustment, which reduces pressure imparted to the fluid and, in return, reduces power consumption.
A Market Driven by Smarter Operations
Adopting VSDs isn't just a trend; it's a fundamental shift in how industries think about motor control. The global VFD market hit USD 28.38 billion in 2024, a clear sign of just how vital this technology has become in manufacturing, HVAC, and material handling.
And it’s not slowing down. That market is expected to climb to USD 39.67 billion by 2030, all thanks to the relentless push for better energy efficiency and lower operating costs.
With over 300 million motors running in industrial settings worldwide, the potential for improvement is staggering. For anyone involved in industrial capital projects, understanding this technology is no longer optional—it's how you stay competitive. You can read the full research about VFD market growth to see the numbers for yourself. This is about more than just a component; it's about a smarter, leaner way to power your operations.
How a Variable Speed Drive Actually Works
So, how does one of these drives actually get the job done? While the inner workings involve some pretty complex electronics, the core concept is refreshingly simple.
Think of a VSD as a power conditioning expert for your motor. It takes the raw, fixed "one-size-fits-all" power from the utility grid and meticulously reshapes it into the perfect, custom-tailored power your motor needs to run at any given speed.
This whole transformation happens in three key stages. Let's imagine you're managing a water supply: the AC power coming in is like a wild, unpredictable river, but your motor needs a perfectly steady and controlled flow to work right. The VSD is the sophisticated dam and valve system that tames that river.
Stage 1: The Rectifier – Taming the Current
First up, the incoming power hits the rectifier. Its only job is to take the alternating current (AC) from the grid and convert it into direct current (DC). In our water analogy, the rectifier is like a dam with a series of one-way gates (diodes) that capture the river's chaotic flow and funnel it into a large reservoir.
A typical three-phase VSD uses six of these diodes, two for each electrical phase. As the AC sine wave for each phase swings from positive to negative, the diodes open and close, letting only the positive voltage pass through. This creates a rough, pulsating DC voltage—like waves filling our reservoir.
Stage 2: The DC Bus – Smoothing Things Out
Once converted, that pulsating DC power flows into the DC bus. This is our reservoir. Its key components are large capacitors that act like shock absorbers, smoothing out the ripples from the rectifier. The capacitors store this electrical energy, soaking up the peaks and filling in the troughs.
What you're left with is a clean, stable DC voltage, primed and ready for the final step. It's worth noting that the voltage here is usually higher than what came in; for a 480V AC system, you'll often see around 650V DC on the bus. This stable reserve of power is absolutely vital for the drive's performance.
At its heart, a VSD is a power manipulator. It converts incoming AC power to a stable DC form, then flips that DC back into a brand new, perfectly controlled AC waveform. This gives you precise control over both the frequency and voltage sent to the motor.
This simple flow shows how a VSD translates a common factory problem into a real, tangible cost-saving solution.
The path from the factory to the piggy bank makes it clear—this technology has a direct and positive impact on your bottom line.
Stage 3: The Inverter – Building the Perfect Waveform
The final and most critical stage is the inverter. This is where the magic really happens. The inverter takes that smooth DC power from the bus and skillfully converts it back into a variable AC output for the motor. Think of it as a set of highly advanced, computer-controlled valves on our reservoir, releasing water in precise, rapid-fire pulses to create a completely new, custom-designed river flow.
This section is built around powerful electronic switches, usually Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistors (IGBTs), that can flip on and off thousands of times per second. By controlling the exact timing and duration of these pulses, the VSD constructs a simulated AC sine wave. This technique is known as Pulse Width Modulation (PWM).
What does this three-stage process give you?
- Total Speed Control: By changing how fast the IGBTs switch, the inverter creates any frequency it wants. Since an AC motor's speed is tied directly to frequency, you now have complete control.
- Optimized Voltage: By adjusting the width of the pulses (how long the switches stay on), the drive dials in the perfect output voltage, ensuring the motor gets just the right amount of power for any speed.
- Pinpoint Precision: This ability to build a perfect AC waveform from scratch gives you unparalleled command over your motor's acceleration, deceleration, and running speed.
By mastering this AC-to-DC-to-AC conversion, a VSD turns a simple AC motor into a highly precise and incredibly efficient machine. To explore these foundational concepts further, check out our guide on variable frequency drive basics. This process is the secret behind a VSD's power and effectiveness.
What VSDs Actually Do for You on the Plant Floor
It’s one thing to understand the theory behind a variable speed drive, but it’s another thing entirely to see what it can do for your operation. This is where the real value hits home. The benefits go way beyond just changing a motor's speed—they deliver real, measurable returns that you can take to the bank.
Two advantages, in particular, are total game-changers for any industrial facility: massive energy savings and far superior process control. For any plant manager or engineer focused on the bottom line, these benefits are impossible to ignore. They offer a direct line to lower operating costs and a more reliable, productive plant.
Slashing Your Energy Bills
If there’s one single reason to get on board with VSDs, it’s the incredible potential for energy savings. Motor-driven systems are energy hogs, often accounting for 25% to 50% of a facility's total electricity bill. The old way of controlling a pump or fan was to run the motor at full tilt and then use a damper or valve to choke back the flow. It’s a brutally inefficient method.
Think of it like driving your car with one foot slammed on the gas and the other on the brake just to manage your speed. It's pure waste.
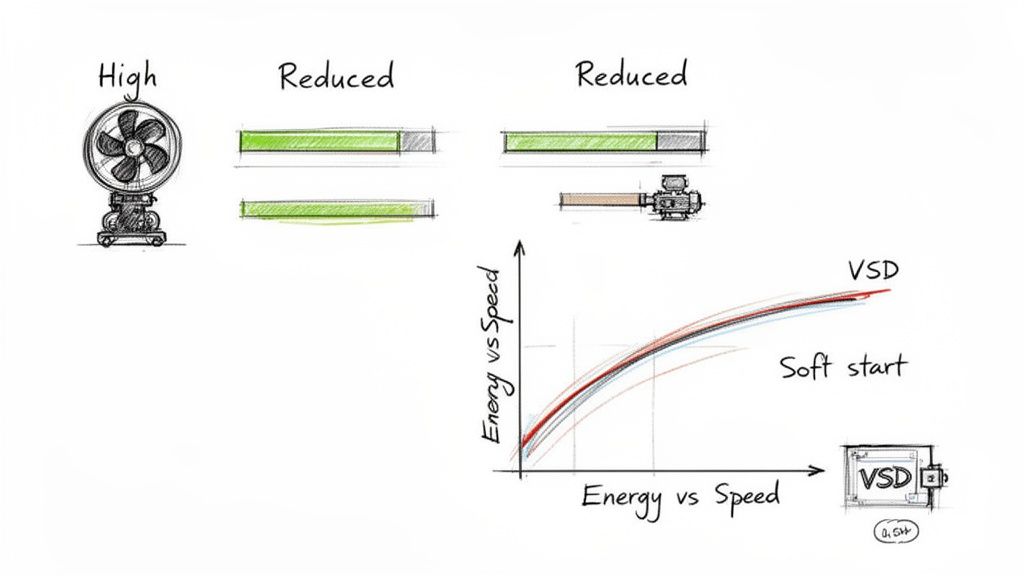
A VSD gets rid of that waste by simply slowing the motor down to match the exact demand. This is where the Affinity Laws for fans and pumps come into play, and they reveal a powerful truth about the relationship between speed and power. These laws show that a motor's power draw varies with the cube of its speed.
What does that cubic relationship mean? It means even a small drop in motor speed creates a huge drop in energy use. For instance, slowing a fan's speed by just 20% (to 80% of its max) can slash its energy consumption by nearly 50%.
That’s the secret sauce. Instead of fighting a full-speed motor, you’re only ever using the precise amount of power you need. This doesn't just cut your electricity bills; it shrinks your carbon footprint, helping you hit sustainability targets while boosting your bottom line. You can dig deeper into the numbers in our full guide on how VFDs generate substantial energy savings.
Extending Equipment Life Through Gentle Control
Beyond saving money on power, VSDs are just plain kinder to your equipment, reducing mechanical stress and making everything last longer. A standard motor starts "across-the-line," which means it gets hit with a massive, instant jolt of full voltage and current. It’s like hitting your machinery with a sledgehammer every time it starts up.
This sudden inrush of current—often 600% or more of the motor's normal running current—sends a shockwave of torque through the entire system, causing all sorts of wear and tear.
A VSD, on the other hand, provides a "soft start." It gently ramps the motor's speed up from a standstill to its target. This smooth acceleration eliminates the mechanical shock that destroys:
- Belts and Couplings: Prevents them from stretching, slipping, and failing prematurely.
- Gears and Gearboxes: Reduces the harsh stress on gear teeth and internal parts.
- Bearings: Minimizes the impact that leads to pitting and eventual failure.
- Piping Systems: Stops "water hammer" and other hydraulic shocks in fluid systems.
This gentle handling means less maintenance, fewer surprise breakdowns, and a longer, more predictable life for your most critical assets. The reduction in downtime alone is often enough to justify the investment in a drive.
Achieving Pinpoint Process Control
Finally, VSDs give you a level of precision that mechanical controls can't even dream of. By allowing you to make exact speed adjustments, a drive can fine-tune a process to boost quality, cut down on waste, and improve consistency across the board.
The table below breaks down how this plays out in a few common scenarios.
VSD Benefits Across Industrial Applications
| Application Area | Primary Benefit | Operational Impact |
|---|---|---|
| HVAC & Pumping Systems | Energy Efficiency | Dramatically reduces power consumption by matching fan/pump speed to real-time heating, cooling, or flow demands. |
| Conveyor Systems | Synchronization | Ensures precise speed matching between different sections of a production line, preventing bottlenecks and material damage. |
| Mixers & Agitators | Product Quality | Allows for variable mixing speeds to achieve perfect consistency for different recipes or batch phases. |
| Winders & Unwinders | Tension Control | Maintains constant tension on materials like paper, film, or wire, preventing stretching, snapping, and waste. |
This kind of control is invaluable in any application that needs to be just right. By integrating a VSD, you’re turning a dumb, fixed-speed motor into an intelligent, responsive part of your operation. You get better products, less waste, and a more agile facility all around.
How to Select the Right Variable Speed Drive
Picking the right variable speed drive isn’t as simple as matching the horsepower on the motor's nameplate. To get it right, you really have to dig into the details of the motor, the job it's doing, and the environment it lives in. Nailing these specifics is the key to a drive that performs reliably and safely for the long haul.
Get this part wrong, and you’re looking at nuisance trips, fried equipment, or worse. A systematic approach helps you specify a VSD that’s a perfect match for your application, saving you from costly mistakes and frustrating downtime. It’s all about building a solid, dependable motor control system from the ground up.
Match the Drive to Your Motor
First things first: look at the motor. Not all motors play nice with VSDs, and hooking one up to a motor that isn't ready for it is just asking for trouble. The simulated AC waveform a VSD creates—with its rapid-fire voltage pulses—is incredibly tough on standard motor windings.
This is exactly why you need to check if your motor is inverter-duty rated. These motors are built with beefed-up insulation systems designed to handle the high voltage spikes and fast switching that VFDs throw at them. If you use a standard motor, you risk the insulation breaking down and shorting out the motor way ahead of its time.
Once you’ve confirmed the motor’s rating, you need to grab some key data off the nameplate to program the drive correctly:
- Full Load Amps (FLA): This is non-negotiable. The drive’s continuous current rating absolutely must be higher than the motor's FLA.
- Voltage and Frequency: Make sure the drive’s voltage matches your system (like 480V) and the motor’s design frequency (usually 60 Hz in the US).
- Motor Speed (RPM): This helps the drive dial in the V/Hz pattern for the best possible performance.
Analyze Your Application Load Profile
Next up, what kind of work is this motor actually doing? Different jobs put different demands on a motor, and VSDs are built to handle them differently. The two big categories you'll hear about are variable torque and constant torque.
A variable torque (VT) load is what you see with centrifugal pumps and fans. With these, the torque needed to spin the equipment skyrockets as the speed increases. Since you rarely need full muscle at low speeds, a VT-rated drive is the perfect, most economical choice.
On the flip side, a constant torque (CT) load needs pretty much the same amount of torque whether it's crawling or running full out. Think of a conveyor belt or a positive displacement pump. These applications need a drive with a much more robust overload capacity to handle that heavy lifting, especially at startup and low speeds. Luckily, many modern drives are dual-rated, so you can just select VT or CT mode during setup.
This choice is critical. A variable torque drive is a smart, cost-saving move for a fan, but putting that same drive on a heavy-duty conveyor is a recipe for constant overload faults and a system that just won't run.
Consider the Operating Environment
Where is this VSD going to live? The physical environment is a huge factor in a drive's lifespan and safety. You have to choose a drive with the right NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association) enclosure rating to shield its sensitive electronics.
A NEMA 1 enclosure is fine for a clean, dry control room. But if the drive will be out on the floor where there’s dust or a risk of light splashing, you’ll need to step up to a NEMA 12 enclosure. And for places that get regular washdowns, like in food processing, a NEMA 4X enclosure is a must to protect against corrosion and high-pressure water.
Don’t forget about air. VSDs kick off a lot of heat, and overheating is one of the top reasons they fail. Make sure the spot you choose has enough airflow around the drive's heatsink, and always follow the manufacturer's specs for clearance space.
Address Power Quality Concerns
Finally, be aware that a VSD can introduce electrical "noise"—also known as harmonics—back into your power system. This can mess with other sensitive electronics in your facility. For big VSD installations, you might need a full-blown harmonic study, but for most smaller drives, there's a simple fix: a line reactor.
A line reactor is basically a big coil you install on the input side of the VSD. It helps smooth out the current the drive pulls from the line, which cuts down on harmonic distortion. It also adds a great layer of protection for the VSD against voltage spikes from the power grid. It's a cheap piece of insurance that adds a ton of stability.
While a VSD is great at managing motor acceleration, sometimes you might be interested in a different approach. You can learn more about what is a soft starter in our detailed guide.
Best Practices for VSD Installation and Commissioning
A top-of-the-line variable speed drive is only as good as its installation. You can have the best drive in the world, but without a solid installation and a methodical startup, you’re setting it up for premature failure. Getting these foundational steps right is non-negotiable for anyone looking to build a reliable system.
Frankly, even the most advanced VSD is vulnerable to common, everyday issues on the plant floor. A proper installation isn't just about hooking up wires; it’s about creating a stable home for the drive to do its job. That means paying just as much attention to electrical noise, heat, and physical placement as you do to the power connections.
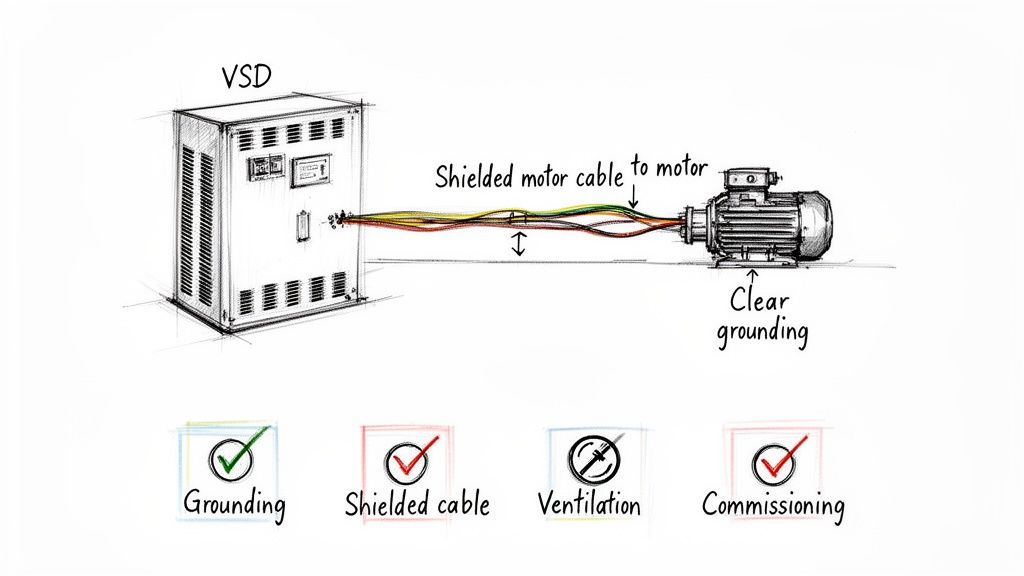
Core Installation Guidelines
Before you even think about flipping the switch, a few installation basics will prevent the vast majority of problems down the line. Think of this as laying the groundwork. Time and again, we see nuisance trips and early component failures that trace back to skipping these simple but critical steps.
First and foremost, proper grounding is your number one defense against electrical noise. The high-speed switching inside a VSD is powerful, but it can create interference that messes with other sensitive equipment. A solid, low-impedance ground gives that noise a safe path away from everything else.
Next, you absolutely must use shielded motor cables. That cable running between the VSD and the motor is basically a giant antenna broadcasting electrical noise. Shielded VFD cable traps that interference, but only if you ground the shield correctly at both the drive and the motor.
Finally, you have to deal with heat. VSDs get hot, and cooking a drive with poor ventilation is one of the fastest ways to kill it. Always follow the manufacturer's clearance specs to give it breathing room. Getting cool, clean air flowing across the heatsink is the key to a long service life.
A Methodical Commissioning Process
Once the drive is installed right, it's time for commissioning—the startup. This is where you teach the drive how to play nice with your motor and application. Rushing this part is a classic mistake that leads to poor performance or, even worse, damaged equipment.
Follow these key steps for a startup that won't give you headaches later:
- Initial Power-Up Checks: Before you go live, double-check that your input voltage is correct and every single connection is tight. A loose wire can cause arcing and catastrophic failure.
- Enter Motor Nameplate Data: This is the most important part of programming. You have to accurately punch in the motor’s Full Load Amps (FLA), voltage, RPM, and horsepower. The drive uses this info for all its motor protection and control logic.
- Perform an Autotune: Nearly all modern drives have an autotune function. Use it. This lets the VSD "learn" the motor's unique electrical profile, which allows it to build a super-accurate model for the best possible torque and current control.
- Set Ramps and Speed Limits: Program your acceleration and deceleration times to match what the machine needs. A smooth ramp-up is easier on your mechanics, and setting min/max speed limits protects your process from running too fast or too slow.
Commissioning is not just about making the motor spin. It's about fine-tuning the drive to the specific load, ensuring the system runs efficiently, reliably, and safely under all operating conditions. Skipping steps here will lead to problems down the road.
When you put in the time for a thorough installation and a systematic startup, you’re building a foundation for a truly robust VSD system. That initial effort pays for itself many times over with less downtime, better performance, and a longer life for your entire system.
Keeping Your VSD System in Top Shape
A VSD that's installed properly is designed to go the distance, but like any piece of high-performance gear, its real-world reliability comes down to smart maintenance and quick troubleshooting. A little bit of proactive attention can make all the difference. In fact, a simple, repeatable maintenance routine is your best bet for preventing the most common failures and keeping your operations humming along without costly surprises.
And when problems do pop up? Knowing how to quickly read the drive's fault codes is the key to slashing downtime. Instead of playing a guessing game, you can let the VSD's own diagnostics point you straight to the issue. This guide is your playbook for doing both.
A No-Nonsense Preventive Maintenance Checklist
Think of regular inspections as your first line of defense. Most VSD issues don’t just happen out of the blue; they build up over time. Catching them early is how you avoid a full-blown breakdown down the road.
A good PM plan doesn't have to be complicated. It really just needs to focus on the three biggest enemies of any VSD: heat, contamination, and loose connections.
Here’s a simple checklist to get you started:
- Look Around: Make a habit of visually checking for signs of overheating—things like discolored components or wiring. You'll also want to make sure the drive's internals are clean and free of dust, debris, or any moisture that could cause a short.
- Check Your Connections: Vibration and normal heating and cooling cycles can work electrical connections loose over time. Get in there and routinely confirm that all the terminal screws for both power and control wiring are snug. A loose connection is just an arc waiting to happen.
- Keep an Ear on the Fan: The cooling fan is absolutely critical. Listen for any weird noises, and make sure it’s spinning freely. A failing fan is one of the most common reasons for overheating, which is hands-down the #1 killer of VSDs.
What Your VSD Is Trying to Tell You: Common Fault Codes
When a VSD trips, it's not actually failing—it's doing its job by protecting itself and your motor. That fault code flashing on the display is an incredibly valuable clue. Understanding what these codes mean is the first step to becoming a troubleshooting pro.
A classic troubleshooting scenario is an overvoltage fault that happens during deceleration. This almost always means the motor is acting like a generator and pushing too much voltage back into the drive. The fix is often as simple as increasing the ramp-down time or adding a dynamic braking resistor.
Let's break down two of the most common faults you'll run into:
Overcurrent (OC): This code pops up when the drive detects a current spike that goes above its rated limit.
- What's a Likely Cause? It could be a sudden, heavy change in the load, a short circuit somewhere in the motor or its cabling, or an acceleration ramp that’s just too aggressive for the application.
- What Should You Do? Start by inspecting the motor wiring for any damage. Then, check the equipment being driven for any mechanical binding or jams. If everything looks good, try increasing the acceleration time to give the motor a smoother start.
Overvoltage (OV): This fault means the DC bus voltage inside the drive has climbed above its safe operating level.
- What's a Likely Cause? Sometimes it's due to high incoming line voltage from the utility, but more often, it's caused by the rapid deceleration of a load with a lot of inertia (like a heavy fan or flywheel).
- What Should You Do? First, measure your incoming AC voltage to make sure it’s within the drive's specified range. If the fault only happens during ramp-down, simply increase the deceleration time. For applications that genuinely need fast stops, you'll probably need to install a dynamic braking resistor to burn off that excess energy.
Got Questions About Variable Speed Drives? We’ve Got Answers.
Let's wrap up by tackling a few of the questions we hear all the time when folks are planning a VSD project. Getting these details straight can clear up a lot of confusion and make your implementation much smoother.
Can I Slap a VSD on Just Any Old Motor?
Not if you want it to last. Your standard, off-the-shelf motor just isn't built to handle the unique electrical stress from a VSD. The drive's high-frequency voltage pulses can eat away at the motor’s winding insulation over time, leading to premature failure.
For reliable, long-term operation, you absolutely need an inverter-duty rated motor. These are specifically designed with beefed-up insulation systems that can take the punishment.
What's the Real Difference Between a VSD and a VFD?
You'll hear these terms thrown around a lot, and honestly, they're often used to mean the same thing in the context of AC motors. VFD, or Variable Frequency Drive, is the more precise term because it describes how the drive controls speed—by changing the frequency of the power sent to the motor.
VSD, or Variable Speed Drive, is a broader umbrella that can also cover DC drives or other methods of speed control. But let's be practical: in today's industrial world, if someone says VSD, they're almost certainly talking about a VFD.
How Much Energy Can I Really Save with a VSD?
The potential here is huge, especially for fan and pump systems. It all comes down to a neat bit of physics called the Affinity Laws, which state that power consumption is tied to the cube of the motor's speed.
What does that mean in the real world? It means a small tweak in speed leads to a massive drop in energy use. For instance, dialing back a fan’s speed by just 20% can slash its energy consumption by nearly 50%. That's how you get a quick payback on your investment.
Do I Always Need a Line Reactor?
While it might not be strictly mandatory for every single installation, think of a line reactor as cheap insurance for your drive. We highly recommend it.
A reactor sits on the incoming power line and does two critical jobs: it protects your VSD from power surges and spikes, and it cleans up the harmonic distortion the drive sends back into your system. This simple addition boosts reliability and improves the overall health of your entire electrical network.
Ready to get precise control over your motors and start banking those energy savings? The team at E & I Sales has the expertise to help you select, design, and integrate the right VSD solution for your plant. Get in touch with us to start your project.

