Predictive maintenance is a pretty simple concept at its core: use real-time data and a bit of smarts to see equipment failures coming before they shut you down. It’s all about getting ahead of the problem.
This approach lets your maintenance crew schedule repairs during planned downtime instead of scrambling to fix things after a catastrophic failure. It’s a move away from reactive, break-fix cycles and toward preventing costly disruptions in the first place, which drops right to your bottom line through significant cost savings and way better efficiency.
Why Predictive Maintenance Is a Game Changer for Manufacturing
Let's cut through the buzzwords and talk numbers. Unplanned downtime isn't just a headache; it's a massive financial drain. Every minute a critical production line sits idle, you're losing money on output, wasting material, and paying for labor that can't work.
This is exactly the problem predictive maintenance was designed to solve.
It fundamentally changes how you think about maintenance. Instead of waiting for a motor to seize or a conveyor to grind to a halt, you’re using technology to constantly listen to the health of your equipment.
The Staggering Cost of Reactive Maintenance
The real gut punch of unplanned downtime is the domino effect it creates. Think about it: a single bearing failure in a critical motor can bring an entire production line to its knees. Suddenly, you're facing missed deadlines, unhappy customers, and emergency repair costs that are always, always higher than planned work.
Siemens actually put a number to this, estimating that manufacturers lose a staggering $260 billion annually because of unplanned downtime.
The flip side? The same research shows that facilities putting predictive maintenance to work are cutting those maintenance costs by 40% and slashing unplanned machine downtime by up to 50%. You can dig deeper into these downtime reduction findings yourself. This isn't just a small improvement; it's a real competitive edge.
How Predictive Maintenance Delivers Tangible ROI
The return on a well-executed predictive maintenance program is crystal clear. When you can see failures coming, you can schedule repairs with surgical precision, which means you're not wasting labor or tying up cash in spare parts you don't need yet.
This leads to some serious benefits:
- Drastic Downtime Reduction: Catching problems early means you can schedule fixes during planned shutdowns. Unexpected stops become manageable tasks.
- Lower Maintenance Costs: Proactive repairs are just cheaper. You avoid overtime labor and the premium you pay for rush-ordered parts.
- Extended Asset Lifespan: Equipment that's properly monitored and maintained simply runs better and lasts longer. You get more out of your capital investments.
- Improved Safety: Identifying potential failures before they become catastrophic helps prevent accidents and makes the plant floor a safer place to be.
For the OEMs and system integrators out there, this is where you can add huge value. Building predictive maintenance capabilities directly into your custom UL control panels and motor control systems transforms a standard electrical package into an intelligent asset that actively protects your customer's operation.
The bottom line is that predictive maintenance isn't just for the big guys anymore. With IIoT sensors and cloud analytics becoming so accessible, it’s now a vital tool for any facility that's serious about running a tight ship. It's about turning data into decisions and building a more resilient, efficient, and profitable operation.
Building Your Predictive Maintenance Technology Stack
Putting together the right technology for predictive maintenance can seem overwhelming. But really, it’s about picking practical tools that solve specific problems on your factory floor. You don't need a gold-plated, overly complex system from the get-go. What you need is a solid foundation that gets the right data and turns it into clear instructions for your maintenance crew.
This blueprint breaks down the core pieces you'll need, from the sensors on the machines to the software that ties into your daily operations.
Starting with the Right Sensors and Gateways
It all starts with data. And that data comes from sensors. Choosing the right sensor is everything; you have to pick one that can actually measure the specific failure you’re trying to get ahead of.
- Vibration Sensors (Accelerometers): These are the absolute workhorses for anything that spins—motors, pumps, fans, you name it. They pick up on imbalances, misalignments, and bearing wear way before a failure becomes catastrophic.
- Thermal Sensors (Infrared): Heat is the classic tell-tale sign of trouble. Whether it’s a loose connection in an electrical cabinet or friction in a mechanical system, thermal sensors will spot it.
- Ultrasonic Sensors: These are fantastic for hearing things humans can't. They detect high-frequency sounds that point to compressed air leaks, electrical arcing, or the very first signs of bearing degradation.
Once a sensor grabs that raw data, it has to go somewhere. That's the job of an IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) gateway. Think of it as the bridge between your physical equipment and your digital systems. It pulls data from multiple sensors and shoots it securely over to your network.
Edge vs. Cloud Analytics: Where to Process Your Data
With data streaming in, you’ve got a big decision to make: where do you analyze it? This choice between edge and cloud computing really impacts your costs, response time, and security.
Edge computing means you process the data right there on or near the factory floor, using things like industrial PCs or smart gateways. This is your go-to when speed is non-negotiable. For instance, if a high-speed packaging machine needs an immediate shutdown signal, you can’t wait for data to travel to the cloud and back.
Cloud computing, on the other hand, is all about sending your data to a remote server for some serious number-crunching. This is perfect for spotting long-term trends across your entire plant and using powerful machine learning models that need massive processing power.
Deciding between the two depends heavily on your specific application's needs for speed, cost, and security.
Edge vs Cloud Analytics for Predictive Maintenance
| Factor | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Very low (milliseconds) | Higher (seconds) |
| Bandwidth Use | Minimal | High |
| Initial Cost | Higher (hardware on-site) | Lower (subscription-based) |
| Scalability | More complex to scale | Easily scalable |
| Data Security | Data stays on-premise | Requires robust cloud security |
Honestly, a hybrid approach often works best. Let edge devices handle the urgent, time-sensitive alerts on the floor, while the cloud crunches data in the background to build smarter, more refined predictive models over time.
Integrating with Your Existing Systems
A predictive maintenance system that doesn't talk to anything else is just a science project. Its real value is unlocked when it integrates smoothly with the tools your team already relies on.
The ultimate goal is to create a closed loop: a sensor detects an anomaly, the analytics platform confirms a pending failure, and a work order is automatically generated in your CMMS with all the necessary details.
This kind of integration is where the efficiency gains happen. When your predictive data flows straight into your CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management System) or ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) software, you kill manual data entry and make sure alerts never get lost in the shuffle. It’s what turns a prediction into a scheduled, proactive repair.
As you build out your tech stack, it’s worth checking out the top predictive analytics software solutions to see what’s out there. Many of these platforms come with ready-made connectors for common CMMS and ERP systems, which can save a ton of headaches.
For system integrators and OEMs, the custom UL control panel is the perfect place to bring all this together. A well-designed panel can house the IIoT gateways, edge hardware, and motor controls in one neat, compliant package. It simplifies installation and gives your customers a standardized, scalable solution. You can dive deeper into modern industrial controls and automation to see how it's done. By building the technology right into the control system, you're delivering a turnkey product that’s ready for predictive maintenance from day one.
Developing a Data Strategy That Actually Works
So you’ve got the shiny new sensors and a gateway ready to go. That's a great start, but the real power behind a winning predictive maintenance for manufacturing program isn't the hardware—it's having a smart data strategy. Without one, you’re just collecting a mountain of digital noise. A solid plan is what turns those raw sensor readings into the kind of clear, actionable intelligence that stops downtime in its tracks.
This isn't about trying to boil the ocean. The key is to be surgical. Your first move should be to zero in on your most critical assets. Forget monitoring everything at once. Pinpoint the machines whose failure would trigger the biggest operational and financial migraines. That’s your starting line.
Identifying Critical Assets and Failure Modes
Once you've got your list of VIP equipment, the next question is simple: how do they usually break? Every machine has its own quirks and common failure points. A centrifugal pump, for instance, might be notorious for bearing wear or seal failure. A robotic arm, on the other hand, might be more prone to gearbox trouble or actuator drift.
This is where you bring in your veteran maintenance techs. These folks have invaluable "tribal knowledge." They know which machines are the real troublemakers and have learned to spot the subtle warning signs over years of hands-on experience. Getting these specific failure modes documented is absolutely crucial—it tells you exactly what data you need to hunt for.
From there, you need to establish a clear baseline of what "normal" operation looks like for each asset. This means capturing operational data—vibrations, temperatures, current draw—while the machine is running perfectly. This baseline becomes your golden standard, the benchmark you'll measure everything against.
Key Takeaway: A killer data strategy starts with quality, not quantity. Focus on capturing the right data from your most critical assets to predict their most common and costly failures. This targeted approach gets you quick wins and builds momentum for the program.
Choosing the Right Predictive Algorithms
With a clean, focused stream of data flowing, you can finally start applying predictive models to find the patterns that scream "impending failure." The algorithm you pick really depends on the complexity of the machine and its failure mode.
- Regression Models: These are your go-to for simpler, linear relationships. Think about predicting the remaining useful life (RUL) of a filter based on a steady increase in pressure drop readings. It's a straightforward cause-and-effect scenario.
- Classification Models: These are perfect for sorting an outcome into a few buckets. A classification algorithm could analyze vibration data from a motor and confidently label its state as "healthy," "moderate bearing wear," or "imminent failure."
- Machine Learning (ML) & AI: For the really complex stuff, like a multi-axis CNC machine or a robotic cell, you need to bring in the heavy hitters. Machine learning can juggle dozens of variables at once, detecting subtle, non-linear patterns that no human could ever hope to spot.
A huge part of this is deciding where to run these analytics—on the edge, right next to the machine, or in the cloud. This isn't a trivial choice.
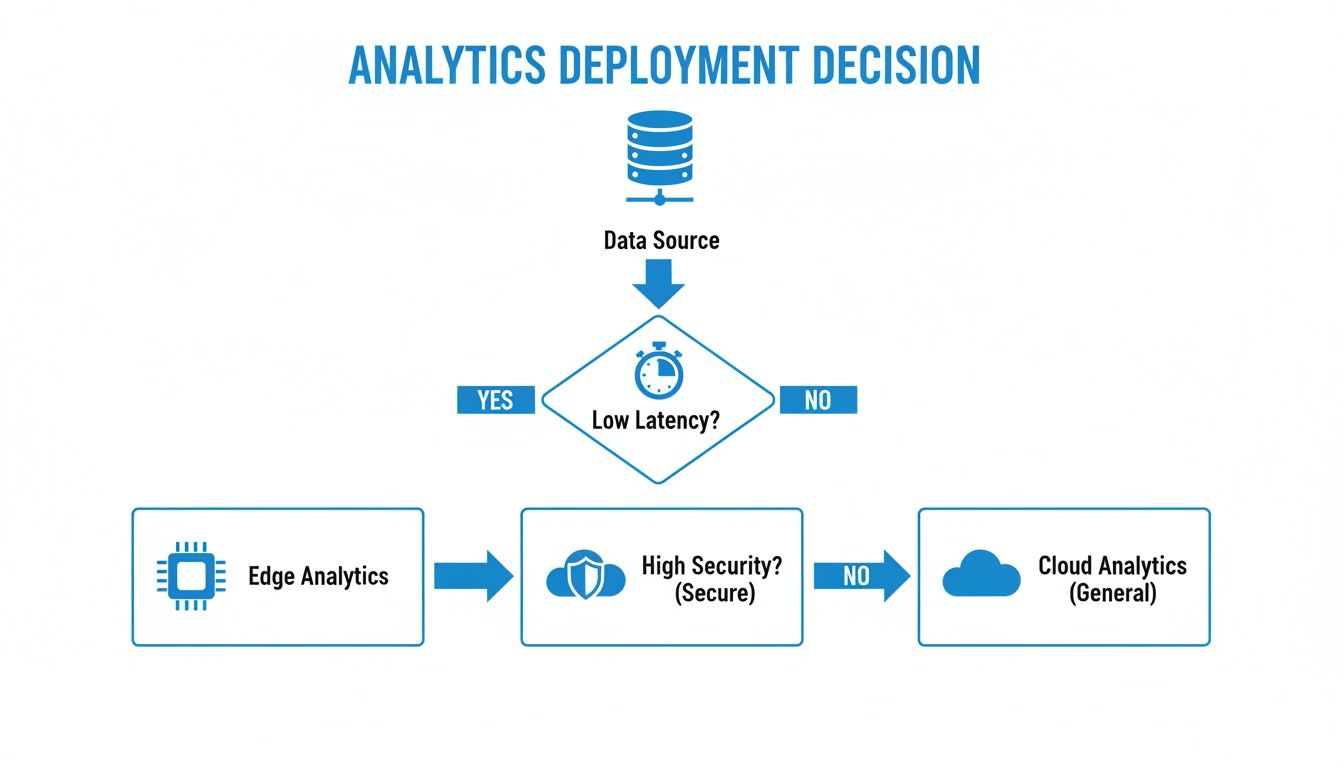
The logic is pretty clear: if you need near-instant responses or you're dealing with sensitive data, edge computing is the way to go. For less time-critical, big-picture analysis where you need massive computational power, the cloud is your best bet.
Turning Predictions into Actionable Alerts
Here’s where the rubber meets the road. All the fancy modeling in the world is useless if it doesn't translate into a clear, actionable alert for your maintenance team. A notification that just says, "Anomaly Detected on Motor 7," is more annoying than helpful.
A good alert gives the team context. It should specify the asset, the suspected problem (e.g., "High probability of outer race bearing fault"), a severity level, and a concrete recommended action. That's the difference between creating more digital noise and actually empowering your team to get ahead of a problem.
This entire data lifecycle—from pinpointing failure modes to generating specific, intelligent work orders—is the backbone of any predictive maintenance for manufacturing strategy that works in the real world. It’s how you ensure your investment doesn’t just spit out interesting charts, but delivers real, tangible results by keeping your lines running.
Launching a Pilot Program to Ensure Success
Jumping headfirst into a full-scale predictive maintenance rollout across an entire facility is a recipe for disaster. I've seen it happen. A much smarter approach is to start small, prove the concept, and build momentum with a well-planned pilot program. This isn't about being hesitant; it's about being strategic.
Think of a successful pilot as your internal case study. It’s your chance to work out the kinks in a controlled environment, show real, tangible value to the people holding the purse strings, and create a scalable blueprint for the rest of the plant. Without it, you risk burning through a lot of capital and losing internal support before the project ever really gets off the ground.
Selecting Your First Critical Assets
First things first: you have to choose where to focus your efforts. Don't try to monitor everything at once. Pick a small group of 3-5 critical assets that give you a good mix of potential challenges and quick wins.
So, how do you pick the right ones? Look for equipment that is:
- Operationally Critical: Pinpoint the machines whose failure brings production to a screeching halt. These are your high-impact targets where preventing even a little downtime delivers immediate, highly visible value.
- Known Troublemakers: Your maintenance team knows which machines are always on their radar. These assets usually have a long and sordid history of failures, which, conveniently, gives your predictive models a rich dataset to learn from.
- Representative of Other Assets: Choose equipment that’s common throughout your facility. If you can prove the system works on one specific model of a pump or motor, it makes the conversation about scaling to dozens of similar assets a whole lot easier.
For instance, a packaging OEM might target a single, high-speed case erector that's notorious for jamming up due to motor fatigue. Or a plant engineer could focus on a critical air compressor that, if it fails unexpectedly, would shut down multiple production lines. These are the specific, high-value targets that make for a compelling pilot.
Defining Clear Success Criteria
Once you have your assets picked out, you absolutely have to define what success looks like. Vague goals like "improve efficiency" just won't cut it. You need concrete, measurable Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to prove the pilot's worth.
Pro Tip: Your single most powerful metric in a pilot program is the "catch." A catch is a documented instance where the system correctly predicted a failure, an alert went out, and your team intervened to prevent an unplanned shutdown. Every single catch is a powerful story of an averted disaster and money saved.
Track your success criteria meticulously. You're essentially building a business case using real data from your own facility.
Key Metrics for a Pilot Program
| Metric | What It Measures | Example Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Number of "Catches" | How many failures were successfully predicted and prevented. | Log at least 3 verified catches in 90 days. |
| Reduction in Unplanned Downtime | The direct impact on production availability for the pilot assets. | Decrease unplanned downtime on pilot assets by 40%. |
| Maintenance Cost Avoidance | The estimated savings from avoiding emergency repairs and overtime. | Show $25,000 in cost avoidance over the pilot period. |
| Alert Accuracy | The ratio of valid alerts to false positives. | Achieve an alert accuracy rate of 85% or higher. |
Creating a Roadmap for Scaling
A successful pilot is just the beginning. The real prize is using its success as a launchpad for a facility-wide rollout. This demands a clear, practical scaling plan that addresses both the technology and, just as importantly, the people.
Your roadmap should be all about standardization. This is where creating pre-configured hardware packages, like custom UL control panels, becomes a massive advantage. Instead of reinventing the wheel for every new asset, you can develop a standardized panel that includes all the necessary sensors, IIoT gateways, and edge hardware. This "plug-and-play" approach drastically cuts down on installation time and engineering costs as you scale.
Don't forget to invest in your team. A common mistake is rolling out new technology without preparing the people who have to use it every day. Develop a structured training program for your maintenance staff. This needs to cover more than just how to respond to alerts; it should touch on the basic principles behind the analytics. For teams coming from a more traditional maintenance schedule, our guide on building a solid preventive maintenance schedule template can provide a great foundational understanding of maintenance planning.
By proving the value on a small scale and then creating a standardized, repeatable process for expansion, you transform predictive maintenance for manufacturing from a one-off experiment into a core operational strategy.
Measuring ROI and Overcoming Common Hurdles
Let's be honest: a predictive maintenance program is just an expensive science experiment until it proves its worth. To get buy-in and keep it, you have to connect the dots between the technology and the bottom line. It's not enough to just say you're preventing downtime; you need to build a rock-solid, data-backed case for it.
This isn't just about satisfying the front office. A clear story of improvement, backed by hard numbers, is what will convince the teams on the shop floor that this new way of working is actually making their lives easier.
Tracking the Right KPIs to Prove Value
Reducing downtime is the obvious win, but it’s only one piece of the puzzle. A truly compelling business case looks at the whole picture—efficiency, asset health, and how effectively your maintenance resources are being used.
Here are the metrics that really matter:
- Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF): This is the classic measure of reliability. When your MTBF starts climbing, you have definitive proof that your equipment is breaking down less often. It’s the most direct validation of your predictive strategy.
- Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE): The gold standard for a reason. OEE rolls up availability, performance, and quality into one powerful number. Improving it shows you're not just stopping failures but actively creating more production capacity.
- Maintenance Cost per Unit: This one really hits home. It ties every dollar you spend on maintenance directly to your plant's output. When this number goes down, you're showing you’re doing more with less.
- Prevented Downtime Incidents: Think of this as your "good catches" log. Every time the system flags a potential failure that you confirm and fix proactively, you log it. Each entry is a tangible win and a story of averted disaster.
You’re not just tracking numbers; you’re quantifying the shift from a reactive, costly break-fix culture to a proactive, value-driven one. When you can show a 20-30% increase in MTBF or a 5-10% jump in OEE, the conversation about ROI becomes much easier.
Navigating Common Implementation Hurdles
Rolling out a predictive maintenance program isn’t always a smooth ride. Even with the best tech, you're going to hit some real-world bumps. Knowing what they are ahead of time—and having a plan—is what separates the successful projects from the ones that stall out.
The industry is moving this way, but old habits die hard. While 30-40% of plants are now using predictive maintenance, a whopping 71% still rely on traditional preventive schedules. But the payoff for pushing through is huge. Teams that make the leap report impressive results: 85% see better downtime forecasting, and 55% of plants report a boost in maintenance staff productivity. As these key maintenance statistics show, tackling the challenges head-on is well worth the effort.
The Challenge of Data Silos and Skills Gaps
One of the first brick walls you’ll likely run into is getting to the data. Critical information is often stuck in separate systems—the control system, the historian, the CMMS—and none of them want to talk to each other. These data silos make it impossible to get a complete picture of asset health.
Your Playbook:
Focus on integration from day one. Use IIoT gateways and modern software platforms with solid APIs to start pulling that data into one place. Don't try to boil the ocean; start with the most critical data points for your pilot assets and build from there.
At the same time, you might realize your team of mechanical wizards isn't as comfortable with data analytics. That’s perfectly normal.
Your Playbook:
Invest in training that’s practical, not academic. Show them what the data means for the machines they know inside and out. Find a technology partner who offers real support, not just a login. Many companies find it incredibly valuable to lean on professional engineering maintenance services to fill that knowledge gap in the beginning.
Overcoming Resistance from Seasoned Teams
This might be the biggest hurdle of all: culture. Your veteran technicians have spent decades relying on their gut—the sounds, the vibrations, the feel of a machine—to know when something's wrong. A new dashboard spitting out alerts can feel like a direct challenge to their experience.
Your Playbook:
Bring them into the fold immediately. Make them a core part of the project, not just the recipients of it. Ask them which assets are the biggest headaches and what the common failure modes are. When the system generates an alert, treat it as a new tool in their toolbox. Frame the conversation collaboratively: "Hey, the data suggests we should look at the bearing on Motor 12. What are you hearing over there?"
This approach builds trust, shows respect for their expertise, and turns potential skeptics into your biggest advocates.
Sorting Out the Details: Your Predictive Maintenance Questions Answered
Even the most straightforward projects come with their share of questions, and shifting to a predictive maintenance model is a big step. We get it. Over the years, we've heard just about every question in the book from OEMs, plant managers, and system integrators.
Here are the answers to the most common ones we field.
Isn't This Just a Fancier Version of Preventive Maintenance?
This is easily the question we hear most, and the difference is fundamental. Think of it this way: Preventive maintenance is all about the calendar. You service a machine every 1,000 hours or every six months, whether it needs it or not. It's a "just-in-case" approach.
Predictive maintenance, on the other hand, is driven by real-world conditions. It uses live data from your equipment to tell you precisely when a component is starting to fail. Instead of changing gearbox oil on a fixed schedule, you change it when the viscosity and particulate data says it's time.
You’re moving from a routine schedule to a data-driven, "just-in-time" intervention. This simple shift is powerful—it can cut maintenance costs by 25-30% by ditching unnecessary work while catching failures before they ever bring the line down.
What's a Realistic ROI for a Program Like This?
The numbers will naturally vary depending on your facility and the specific machines you're monitoring, but the financial case is consistently strong. Most companies see a full return on their initial investment within two years. For critical assets where downtime is catastrophic, we’ve seen projects pay for themselves in under 12 months.
The ROI isn't just a single number; it comes from several places at once:
- Drastically Reduced Downtime: This is the big one. Most plants see unplanned stops fall by 35-45%.
- Smarter Maintenance Spending: Fewer frantic, high-cost emergency repairs and less wasted labor on perfectly healthy equipment.
- Leaner Spare Parts Inventory: Why stock a dozen spare motors when the data shows you'll only need one in the next six months?
- Longer-Lasting Machines: Equipment that operates within its ideal parameters simply has a longer, more productive life—often by 20-40%.
An initial pilot program might run anywhere from $50,000 to over $200,000, but a mature system can deliver a 5x to 10x return on that investment.
Do I Need to Hire a Team of Data Scientists?
Definitely not, especially when you're just getting started. The best predictive maintenance platforms today are built for the people on the plant floor—the reliability engineers and maintenance techs who know the equipment inside and out. These systems come loaded with proven algorithms for common equipment like pumps, motors, and conveyors.
Frankly, your team's hands-on experience is far more valuable at the outset. They’re the ones who can hear a bearing starting to go long before it fails. They understand the real-world context behind the data points. The goal here is to give your existing experts better tools to work with, not to replace them with data analysts. You can always bring in specialized help from a partner as you scale.
What's the Single Biggest Mistake People Make?
Trying to boil the ocean. Hands down, the most common mistake is attempting to monitor every single asset in the plant right out of the gate. This approach is a recipe for disaster. It's incredibly expensive, generates a firehose of data that no one can manage, and makes it impossible to demonstrate a clear win.
Success comes from starting small and being strategic. Pick a handful of your most critical—or most problematic—assets and launch a focused pilot program. Prove the concept, calculate the ROI, and turn your maintenance team into believers. That initial success is what builds the momentum and the business case you need to expand the program across the facility.
At E & I Sales, we're the ones who build the intelligent nerve center for your predictive maintenance strategy. We design and fabricate the custom UL control panels that seamlessly integrate your sensors, motor controls, and data hardware, giving you a rock-solid foundation for success. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your project.

