A Variable Speed Drive (VSD) isn't your typical motor controller. Forget the simple on/off switch; think of it more like the gas pedal in your car, but for industrial-sized machinery. It gives you the power to tell an electric motor exactly how fast to run and how much torque to deliver by finely tuning the voltage and frequency it receives. This precision is the secret to unlocking incredible efficiency in just about any industrial process.
Why a Variable Speed Drive Matters
Let's imagine you need to control the water coming out of a fire hose. Your only options are full blast or completely off. To get just a trickle of water, you'd have to crank a valve halfway closed, fighting against the immense pressure. The pump is still screaming at full power, wasting a ton of energy and putting a massive strain on the entire system.
Believe it or not, this is how a shocking number of industrial motors work—pegged at maximum speed, no matter what the job actually requires.
A variable speed drive completely flips that wasteful model on its head. Instead of running the motor at 100% and then mechanically choking the output, the drive simply tells the motor to slow down to match the real-time demand. It’s a simple concept, but one that has become a cornerstone of modern industrial efficiency, with benefits that ripple out far beyond just speed control.
The Core Advantages of VSDs
When you start looking at a VSD, the business case really boils down to three powerful pillars:
- Massive Energy Savings: This is the big one. By making sure a motor only draws the power it truly needs, VSDs can slash electricity bills. For common applications like pumps and fans, trimming the motor speed by just 20% can cut energy consumption by nearly 50%.
- Tighter Process Control: VSDs deliver silky-smooth acceleration and deceleration, lock in precise speeds, and can even get multiple motors to work in perfect harmony. This level of control means better product quality, less wasted material, and more agile production lines that can adapt on the fly.
- Longer Equipment Life: A motor starting up at full power is like getting rear-ended. It’s a violent jolt, both electrically and mechanically. The soft-start capability of a VSD gently ramps up the motor, eliminating that shock. This saves immense wear and tear on belts, gears, couplings, and the motor itself, which means fewer breakdowns and lower maintenance bills.
A variable speed drive isn't just another component; it's a strategic tool for running a smarter operation. It turns a fixed-speed motor from a blunt instrument into a precision device, optimizing everything from your energy spend to your equipment's reliability.
We're seeing the impact of this technology everywhere. As energy regulations get tighter and automation becomes the norm, the demand for VSDs is exploding. One forecast sees the global market climbing from $21.74 billion in 2026 to $27.24 billion by 2030, all driven by the relentless need to cut operating costs. For industrial plants, this isn't just a trend; it's a path to reducing energy use by 30-60% in variable load applications. You can dig into more of this data on the growing VFD market at ResearchAndMarkets.com.
Let's break down these advantages for a clearer picture of who benefits and how.
Key Benefits of Using a Variable Speed Drive
| Benefit Category | Description | Primary Beneficiary |
|---|---|---|
| Financial | Drastically reduces energy consumption by matching motor speed to load demand, leading to significant savings on electricity bills. | Plant Owners, CFOs |
| Operational | Provides precise control over speed, acceleration, and torque, improving product consistency and reducing process variability. | Production Managers, Quality Control |
| Maintenance | Soft-starting reduces mechanical stress on motors, bearings, and couplings, leading to fewer breakdowns and a longer equipment lifespan. | Maintenance Teams, Reliability Engineers |
| System | Lowers inrush current during motor startup, which reduces stress on the electrical grid and can lower demand charges from utilities. | Facility Managers, Electrical Engineers |
Ultimately, implementing a VSD is a win across the board, creating a more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective operation from the plant floor to the balance sheet.
How a Variable Speed Drive Actually Works
To really get how a variable speed drive gives you such fine-tuned control over a motor, it's best to stop thinking of it as a single box. Instead, picture a miniature power refinery. Its whole job is to take the raw, fixed-frequency AC power coming from the grid and meticulously process it into a custom-tailored power source that's perfect for the motor's needs. This all happens in three key stages.
You'll hear the terms Variable Speed Drive (VSD) and Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) thrown around interchangeably, and for the most part, that's fine. But VFD is technically the more precise term when we're talking about AC motors. The speed of an AC motor is directly linked to the frequency of the power it's fed, so changing the frequency is how we change the speed. It's that simple. That's why VFDs are the go-to for pretty much any AC motor application.
The Rectifier Stage: Intake and Conversion
First up is the rectifier. Think of this as the intake valve for our little power refinery. It grabs the incoming Alternating Current (AC) from your main panel and immediately converts it into Direct Current (DC). It accomplishes this with a set of diodes, which basically act like one-way gates for electricity.
These diodes only let the current flow in a single direction, which lops off the negative half of the AC sine wave. What you're left with is a bumpy, pulsating DC voltage. This is a critical first move, because you can't really do much with a fixed AC frequency. Turning it into DC gives the drive a flexible, raw material it can actually work with.
The DC Bus: The Power Reservoir
From the rectifier, the power flows into the second stage: the DC bus, sometimes called the DC link. This part is like a big holding tank. It’s filled with large capacitors that take the pulsating DC voltage and smooth it out into a clean, stable supply.
This smooth DC voltage is then held in reserve, ready for the final, most critical stage. The stability of this DC bus is everything; it ensures the last part of the process has a perfectly consistent power source to pull from.
A variable speed drive operates by first deconstructing the incoming AC power into a stable DC form, and then meticulously reconstructing it into a new, fully adjustable AC waveform. This two-step conversion is what makes precise speed and torque control possible.
The Inverter Stage: Crafting the Perfect Output
The last stop is the inverter, and this is where the real magic happens. This is the sophisticated blending station of our refinery. The inverter takes that smooth DC power from the bus and uses a set of incredibly fast electronic switches (usually Insulated-Gate Bipolar Transistors, or IGBTs) to chop it up and reassemble it into a brand-new AC waveform.
This technique is called Pulse Width Modulation (PWM), and it involves those switches turning on and off thousands of times per second. By precisely controlling the width and timing of these DC pulses, the inverter can perfectly mimic an AC sine wave at just about any frequency or voltage you command.
This newly crafted AC power is what gets sent to the motor. Need the motor to run at half speed? The inverter whips up a 30 Hz waveform. Need to crank it to full speed? It delivers a 60 Hz waveform. It's this absolute control over frequency that lets a VFD manage motor speed with such incredible precision. To see how this plays out with different motors, take a look at our guide on AC motor variable speed control.
This simple concept map really brings home how a VSD's core function translates into major operational wins.
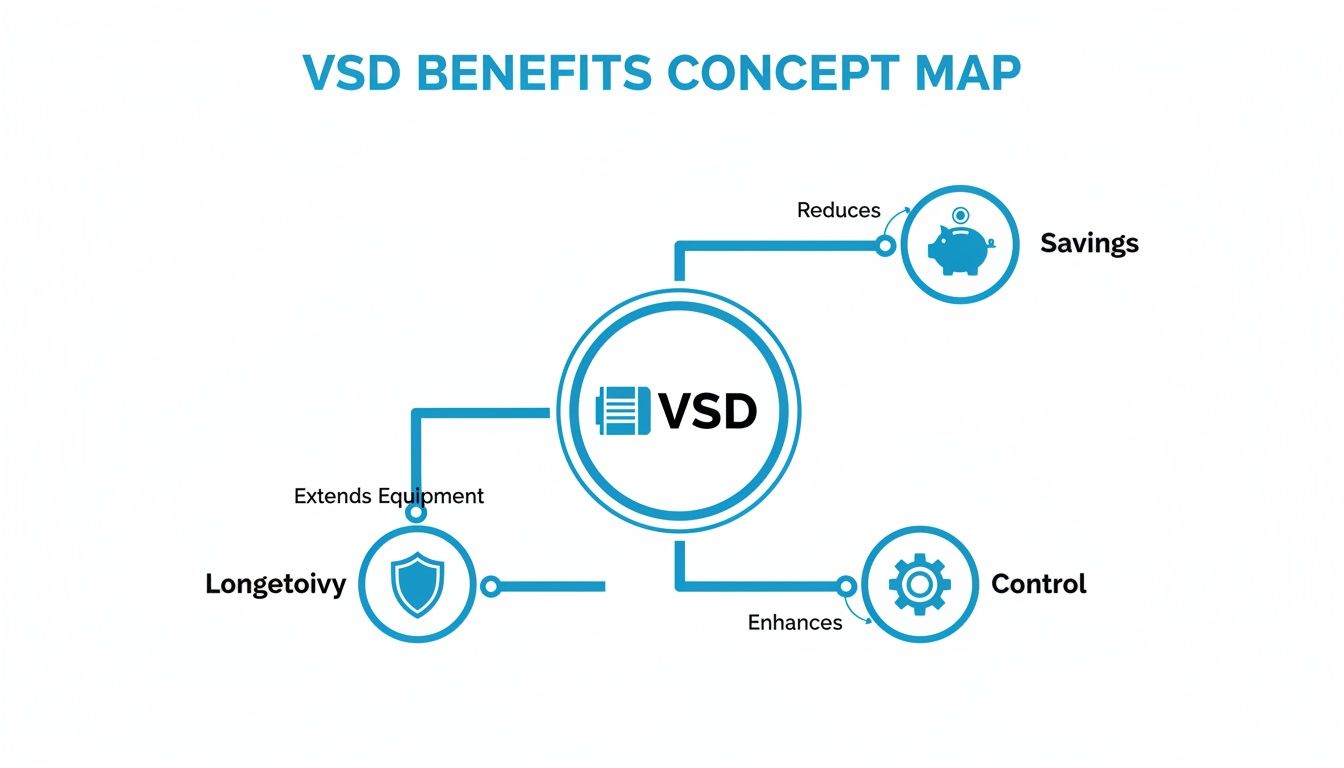
As you can see, the drive’s ability to precisely control a motor directly leads to lower operating costs, much better process control, and a longer life for your equipment.
Where Variable Speed Drives Make the Biggest Impact
The theory is great, but seeing a drive in action on the plant floor is where it all clicks. These aren't some niche, specialized components; they're the workhorses behind the most common—and power-hungry—equipment in almost any facility. Moving away from the old "all or nothing" fixed-speed approach fundamentally changes the game.
Let's dig into the applications where this technology really shines and delivers the biggest bang for your buck. From pumping water to moving products, precise speed control unlocks a whole new level of performance and savings.
Unlocking Savings in Pumps and Fans
Pumps and fans are absolutely everywhere, from the municipal water plant down the road to the massive HVAC system keeping a skyscraper cool. They also happen to be the perfect candidates for VSDs, all thanks to a simple principle called the Affinity Laws.
These laws explain the relationship between a motor's speed and its power consumption in centrifugal applications like pumps and fans. The key takeaway? The relationship isn't linear—it's cubic. That means a small drop in speed leads to a massive drop in energy use.
The Affinity Laws reveal a powerful truth: reducing a fan or pump's motor speed by just 20% can cut its energy consumption by nearly 50%. This disproportionate saving is why VSDs are a game-changer in fluid and air movement applications.
Think about it. The old way involved running a pump at full blast and choking the flow with a valve. That’s like driving your car with one foot slammed on the gas and the other on the brake. A VSD simply tells the motor to slow down to deliver exactly the flow you need. This saves an incredible amount of energy and also reduces the mechanical stress on your pipes, valves, and seals. You can learn more about how this translates to your bottom line in our article on calculating VFD energy savings.
Real-World Application Examples
- Wastewater Treatment: A municipal lift station sees huge swings in flow throughout the day. With a VSD, the pumps can ramp up for the morning rush and then slow to a crawl overnight, perfectly matching demand. This avoids the energy waste and mechanical shock of constantly slamming the motors on and off.
- Commercial HVAC: In a big office building, VSDs on air handlers and cooling tower fans adjust airflow based on real-time temperature and occupancy. It's the same idea behind modern variable speed heat pumps in homes, which deliver huge savings and better comfort.
Achieving Precision with Conveyors and Compressors
While the energy savings with conveyors and compressors aren't quite as dramatic as with pumps, a drive variable speed delivers something just as valuable: process control.
For conveyors, it’s all about synchronization. Picture a bottling line where bottles have to move perfectly from the filler to the capper to the labeler. A VSD ensures every section runs at the exact same speed, preventing jams and spills. It also provides a smooth "soft start," getting rid of that violent jerk that can knock products over and beat up your chains and gearboxes.
Compressors benefit in a similar way. Instead of the inefficient cycle of running full-bore to fill a tank and then shutting off, a VSD matches motor speed to the plant's actual air demand. This gives you a rock-solid, stable air supply while slashing energy costs, especially in facilities where demand is all over the place.
Manufacturing Application Example
In an automotive plant, a VSD-controlled overhead conveyor automatically adjusts its speed to match the assembly line's pace. If the line slows, the conveyor slows right along with it, delivering parts exactly when they're needed. This kind of precise timing minimizes clutter on the floor and smoothes out the entire production flow, proving a drive variable speed is as much a tool for optimization as it is for energy savings.
How to Pick the Right Variable Speed Drive
Choosing the right variable speed drive isn't like grabbing a part off a shelf. It's more like being a matchmaker, pairing a sophisticated piece of technology to the specific personality of your machine. When you get it right, you've laid the foundation for a reliable, hyper-efficient system that just works.
But get it wrong? You're in for a world of headaches—nuisance tripping, poor performance, premature burnouts, and a completely wasted investment.
The whole process starts with the most critical relationship in your system: the bond between the drive and the motor it's going to control. Think of it like a race car. You wouldn't put a minivan's transmission on a Formula 1 engine and expect good results. The drive and motor have to be perfectly in sync.
Matching the Drive to Your Motor and Load
The motor's nameplate is your single source of truth. It's got the non-negotiable data you absolutely need to find a compatible drive. Zero in on these three core stats:
- Full Load Amps (FLA): This is the big one. Your drive must be able to supply at least this much current continuously without breaking a sweat. Always, always pick a drive with a current rating equal to or, even better, slightly greater than the motor's FLA.
- Voltage: Simple but critical. The drive's input and output voltage have to match your building's supply and the motor's rating (e.g., 480V 3-phase). No exceptions.
- Horsepower (HP) or Kilowatts (kW): This is a useful quick reference, but think of it as a secondary check. The FLA is what tells you the motor's real-world current appetite, making it the most accurate number to go by.
Once the drive and motor are on the same page, you have to look at the work the motor is actually doing—the load. Industrial loads aren't all the same; they typically fall into one of two camps.
- Variable Torque Loads: Think of centrifugal pumps and fans. The faster they spin, the more torque they need. Because they barely break a sweat at low speeds, you can often get away with a standard, normal-duty drive, which can save you some money.
- Constant Torque Loads: This is your heavy-lifting crew—conveyors, compressors, and mixers. These machines demand nearly full muscle (torque) even when they're just getting started or running slow. They need a beefier, heavy-duty rated drive that can handle that sustained current demand without flinching.
One of the most common—and expensive—mistakes we see is putting a normal-duty drive on a constant-torque application. The drive will be constantly gasping for air, thermally overloaded, and tripping on faults until it eventually gives up for good. Always match the drive's duty rating to the job at hand.
Don't Forget the Environment (Physical and Electrical)
The world your drive will live in is just as important as the motor it’s wired to. Ignoring its surroundings can sabotage an otherwise perfect setup.
First up, the physical location. A drive living in a pristine, climate-controlled electrical room has a very different life than one getting splashed down on a factory floor. This is where NEMA ratings become your best friend.
- NEMA 1: Your standard indoor enclosure for clean, dry spots.
- NEMA 12: Adds a layer of protection against dust and dripping liquids.
- NEMA 4X: The workhorse for tough-and-tumble environments. It’s built to withstand corrosion and direct water spray, perfect for washdown areas.
Beyond the physical grit, you have to deal with the electrical "noise" called harmonic distortion. It's a natural byproduct of how VFDs work. They create electrical disturbances that can travel back through your power lines and cause bizarre problems for other sensitive equipment.
That’s why adding components like line reactors or harmonic filters is so often a must. A line reactor is basically a big coil that sits on the input side of the drive, smoothing out the current it draws and absorbing a lot of that harmful harmonic noise. It's a simple, cost-effective insurance policy for your drive and your entire electrical system.
This push for greater efficiency and rock-solid reliability is exactly why the VFD market is booming. Valued at USD 28.38 billion in 2025, the global market is on track to hit USD 39.67 billion by 2030, all thanks to the incredible flexibility these drives offer. You can dive deeper into these VFD market trends from Grand View Research. This growth just highlights how critical it is to get the selection right from the start.
To help you keep track of all these moving parts, we've put together a quick checklist.
VSD Selection Checklist
This table breaks down the essential technical criteria to review when you're sizing up a new drive. Think of it as your pre-flight checklist before making a final decision.
| Selection Criterion | Key Considerations | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Motor Compatibility | Check motor FLA, Voltage, and HP/kW on the nameplate. | The drive's ratings must meet or exceed the motor's needs to avoid overload and failure. |
| Load Type | Is it Variable Torque (pumps, fans) or Constant Torque (conveyors, compressors)? | Constant torque loads require a heavy-duty rated drive to handle high current at low speeds. |
| Enclosure Rating | NEMA 1, NEMA 12, NEMA 4X, etc. | The enclosure must protect the drive from dust, moisture, and chemicals in its specific location. |
| Harmonic Mitigation | Do you need a line reactor, DC link choke, or an active harmonic filter? | Unchecked harmonics can disrupt other equipment and damage the drive itself. |
| Braking Requirements | Will the motor need to stop quickly or hold a load? | Applications with overhauling loads may require a dynamic braking resistor to dissipate energy. |
| Control & I/O | How many analog/digital inputs and outputs are needed? | Ensures the drive can interface with your PLCs, sensors, and other control system components. |
| Communications | Does it need to speak EtherNet/IP, Modbus, PROFINET, or another protocol? | Crucial for integrating the drive into a larger automation network for monitoring and control. |
| Environmental Factors | What are the ambient temperature and altitude of the installation site? | Extreme temperatures or high altitudes can require derating the drive (using a larger size). |
Running through these points every time will help you avoid common pitfalls and ensure the drive you choose is a perfect fit, ready for years of reliable service.
Getting Your VSD Installation and Commissioning Right
You can pick the perfect drive variable speed for the job, but if the installation is sloppy, you're setting yourself up for failure. A flawless installation and a careful, methodical commissioning process are what separate a reliable, high-performing system from one plagued with nuisance faults and premature breakdowns.
Getting it right from day one is everything. It's about safety, reliability, and actually getting the energy savings you were promised.
This all starts with the physical install, which is so much more than just bolting a drive to the wall. The foundation you lay here will determine the drive's entire service life.
Foundational Physical Installation Steps
The physical setup is all about controlling the drive's environment—both mechanically and electrically. Paying attention to the small details here will save you massive headaches down the road.
Give It Room to Breathe: VSDs throw off a lot of heat. You absolutely have to respect the manufacturer's specified clearances around the unit. This isn't a suggestion; it's a requirement for proper airflow to prevent overheating and thermal shutdowns. Never, ever stick a drive in a sealed, unventilated cabinet without a real cooling plan.
Separate Your Wires: This one is non-negotiable. The high-power wiring running from the drive out to the motor is electrically "noisy." Always run your low-voltage control wiring (for things like start/stop signals or speed commands) in a completely separate conduit. If you can't, at least keep them several inches apart to stop interference from scrambling your signals.
Ground It Properly: A solid, low-impedance ground connection is your single best defense against electrical noise and a critical safety measure. Don't freelance this part. Follow the manufacturer's guide to the letter, using the correct grounding terminal and wire size to create a clean, direct path to earth ground.
The Commissioning and Startup Sequence
Once the drive is physically in place, it’s time to bring it to life. Commissioning is a deliberate process, a step-by-step sequence where you configure the drive for your specific motor and application. Think of it as introducing the drive to the job it's about to do for the next decade.
A critical part of this is the auto-tune function, a feature on just about every modern drive. The drive sends a series of test signals to the motor to learn its unique electrical personality—its resistance, inductance, and other characteristics.
Getting the auto-tune right is one of the most important things you'll do. It allows the VSD to build a precise mathematical model of the motor, which is the secret to achieving incredible torque control and smooth performance across the entire speed range.
With a successful auto-tune complete, you can dial in the key parameters that are specific to your machine's needs.
- Acceleration and Deceleration Ramps: These settings dictate how fast the motor ramps up to speed and how quickly it slows down. Setting smooth, gradual ramps prevents mechanical shock on equipment like conveyor belts and avoids damaging pressure surges in pumping systems.
- Minimum and Maximum Speeds: Here, you set the operational boundaries. A pump, for instance, might need a minimum speed to maintain flow, while a large fan might have a maximum speed limit to prevent dangerous vibrations.
- Motor Protection Settings: This is crucial. You'll program the motor's full-load amp (FLA) rating directly into the drive. This lets the VSD's internal electronic overload act as a highly intelligent bodyguard for your motor, protecting it far more effectively than a simple old-school thermal overload relay.
This meticulous approach is vital. Variable speed drives are transforming global industries by addressing skyrocketing energy demands, with market projections revealing huge potential for system integrators and plant operators. For industrial facilities, this means VFDs can yield 10-40% energy savings, which is vital amid regulations pushing sustainability. North America's projected USD 4.92 billion U.S. market by 2030 is tied to this power infrastructure modernization, where turnkey services shine. You can explore more about these market projections at Precedence Research.
Finally, don't forget about electrical noise. The high-frequency switching inside a VSD creates harmonics that can mess with other sensitive equipment on your power network. Understanding and managing this is part of a professional installation, which is why we put together a detailed guide on harmonic filters for VFDs.
Following these best practices for your drive variable speed ensures you not only get your system running correctly but also squeeze every bit of performance and life out of it for years to come.
Keeping Your Drive Running for the Long Haul
A variable speed drive is one of the toughest pieces of electronics in your facility, but it’s not set-it-and-forget-it hardware. If you want to protect that investment and sidestep the kind of surprise downtime that ruins a production schedule, you need a smart maintenance plan. The best insurance policy you can have is a simple, consistent routine.
Think of it like taking care of your car. You wouldn't just drive it until the engine seizes and then wonder what went wrong. You perform regular oil changes and checkups to catch small issues before they become catastrophic failures. Your VSD deserves the same level of care.
The good news? The most critical maintenance tasks are often the easiest to perform. It all boils down to creating a schedule for basic cleaning and inspection that your own team can handle with just a little training.
Building a Simple Preventive Maintenance Routine
At its core, a solid VSD maintenance plan is about keeping the drive clean, cool, and connected. Heat and contamination are the two biggest killers of a VSD, hands down. They are the root cause behind a huge percentage of all drive failures. A simple checklist is all you need to keep them at bay.
Here are the essentials for any VSD check-up:
- Walk-Around Inspections: Make it a habit to just look at your drives. Check for dust caked onto the heat sinks, listen for noisy fans, and look for any discoloration on the enclosure that might signal a hot spot.
- Keep It Clean: After a proper lockout/tagout, a little housekeeping goes a long way. Use a vacuum with a non-static attachment and a dry, lint-free cloth to clear out vents, fans, and heat sinks. Whatever you do, don't use compressed air. It can blast conductive dust deep into the circuit boards where it can cause a short.
- Check Your Connections: Vibration and the constant heating and cooling cycles inside a panel can cause electrical connections to work themselves loose. Periodically put a screwdriver or torque wrench on the power and control terminals to make sure everything is snug. A loose wire is a fire hazard waiting to happen.
"The vast majority of drive failures can be traced back to two simple culprits: heat and contamination. A disciplined cleaning and inspection schedule is the single most cost-effective strategy for maximizing the lifespan of any variable speed drive."
What to Do When Fault Codes Pop Up
When a problem does occur, your VSD is smart enough to tell you what's wrong. It will trip on a fault and display a code that gives you a massive head start on troubleshooting. Knowing what the most common codes mean helps your team fix simple issues on the spot and know when it’s time to call in an expert.
Here are a few of the usual suspects:
- Overvoltage (OV): This often happens when a motor is slowing down a heavy load. The motor temporarily acts like a generator and sends a jolt of power back to the drive. You can usually fix this by increasing the decel time or adding a dynamic braking resistor.
- Overcurrent (OC): This is a classic "something's stuck" fault. It could be a jam in the conveyor, an accel ramp that’s too aggressive, or a dead short in the motor or its wiring.
- Overtemperature (OT): If you see this, the drive is getting too hot. The cause is almost always simple: a clogged air filter, a cooling fan that has died, or an ambient room temperature that’s just too high for the drive’s rating.
Got Questions About Variable Speed Drives? We’ve Got Answers.
When you're digging into the world of a drive variable speed, a lot of practical questions pop up. It happens to everyone, whether you're designing a new system from scratch or looking to upgrade an older one. Getting straight answers is what lets you move forward with confidence. Let's tackle some of the most common questions we hear out in the field.
One of the first things engineers ask is, "Can I just slap a VSD onto any old AC motor?" The short answer is, not quite. While most modern three-phase AC motors are built for it, you have to make sure it has an "inverter-duty" rating. This basically means the motor’s internal insulation is tough enough to handle the unique electrical waveforms the drive produces, saving you from a premature burnout.
Understanding Drive Types and Real-World Savings
Another point of confusion we often see is the difference between constant torque and variable torque drives. Here's the secret: it's not really about the drive itself, but the job it's being asked to do.
- Constant Torque: Think conveyors, mixers, or anything that needs the same amount of muscle whether it's running fast or slow. These applications need a heavy-duty drive that can deliver full power at any speed.
- Variable Torque: This is the world of pumps and fans. Their workload drops off dramatically as they slow down. A standard or normal-duty drive is usually perfect for these jobs.
This distinction is huge when it comes to your potential savings. While any drive variable speed will cut down on energy use, the real magic happens in variable torque applications. For pumps and fans, pulling the speed back by just 20% can slash your energy consumption by almost 50%—that's the power of the Affinity Laws at work. With constant torque loads, the savings come from precisely matching speed to the work at hand, which is still a significant win.
The biggest ROI from a variable speed drive always comes from applications where the load isn't constant. Pumps, fans, and blowers are the superstars because their power demand plummets exponentially as you dial back the speed.
So, Do I Really Need a Line Reactor?
Finally, let's talk accessories. "Do I always need a line reactor with my VFD?" is a question we get all the time. While it's not technically required in every single case, it’s a smart move. Think of a line reactor as an inexpensive insurance policy. It acts as a buffer, protecting your expensive drive from voltage spikes and sags from the power grid. Just as important, it cleans up the "noise" or harmonic distortion the drive sends back into your system, protecting other sensitive electronics on the same circuit.
Ready to put the right motor control solution to work for your operations? The experts at E & I Sales provide engineered UL-listed control panels and complete integration services to make sure your project is a success from day one. Learn more at eandisales.com.

