Ever felt the frustrating "slop" or backlash in a machine? That tiny bit of play in a gear or a belt that throws off precision? Direct drive motors are the answer.
Instead of relying on clunky gearboxes, belts, or chains, a direct drive motor connects straight to the load it needs to move. It’s a clean, simple, and incredibly efficient way to transfer power with a perfect 1:1 ratio. This direct connection is a game-changer for precision and reliability in modern automated machinery.
What Is a Direct Drive Motor?
Think about the difference between a high-performance electric car and a standard gas-powered one. In the EV, power flows almost instantly from the motor to the wheels. The gas car, however, sends power through a complex transmission filled with gears and shafts, each one a potential point of failure or energy loss.
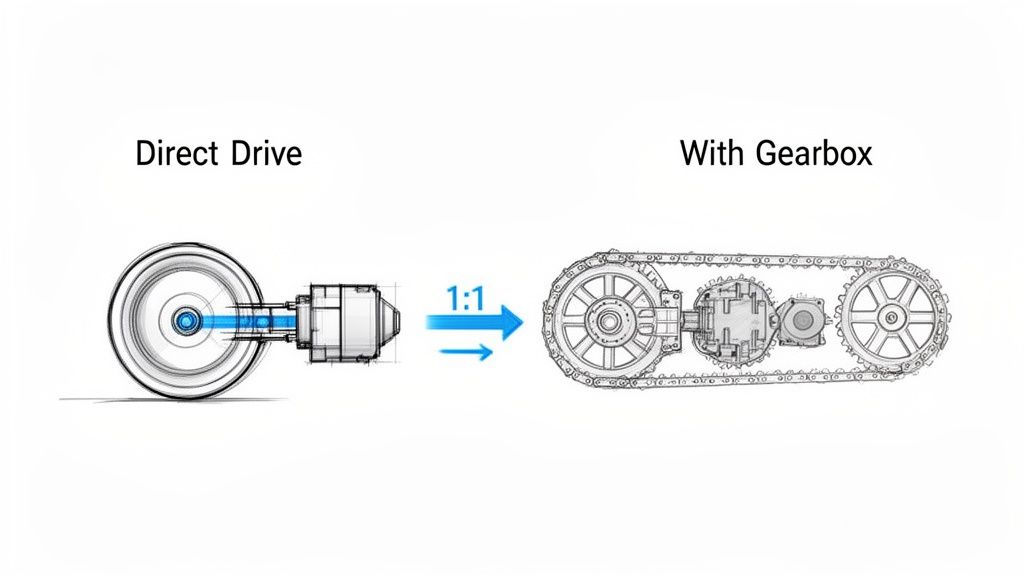
A direct drive motor works like that electric car, giving you an immediate and efficient transfer of energy.
By physically coupling the motor’s rotor directly to the component you’re trying to move, you get rid of all the in-between mechanical parts. This elegant simplicity is its biggest advantage. No gears means no backlash messing with your positioning. No belts means no tensioning, slipping, or replacements to worry about.
The Core Design Philosophy
The leap to direct drive isn't just a small improvement; it's a completely different way of approaching motion control. It's about trading a system of many complicated parts for a single, integrated unit. The payoff is huge:
- Pinpoint Precision: With zero backlash, you get incredibly accurate and repeatable positioning. This is non-negotiable for equipment like CNC machines and high-speed robotics.
- Serious Efficiency: Without the friction from a gearbox or belt system, direct drive motors can hit efficiency ratings over 95%. That's power going straight to the work, not wasted as heat.
- Lower Maintenance: Fewer moving parts means fewer things to wear out, lubricate, or replace. The result? A massive reduction in downtime and labor costs.
- Smaller Footprint: Getting rid of bulky transmissions lets you build smaller, more streamlined machines.
By delivering power straight to the load, a direct drive motor creates a system that is mechanically stiff, highly responsive, and inherently more reliable. This direct connection is the key to achieving a level of performance that traditional systems struggle to match.
The market is taking notice. The global direct drive motors market hit USD 6.5 billion thanks to huge demand from automation and robotics. It’s on track to more than double, reaching USD 12.8 billion by 2033, growing at a solid 7.9% CAGR.
To get a better handle on what makes this technology tick, it helps to look at how performance is squeezed out of other motor types, like the high performance electric motors used in specialized EVs. The same core principles of maximizing torque and efficiency apply. Ultimately, direct drive motors are setting a new bar for modern automation, clearing the way for faster, more precise, and more dependable machinery.
Direct Drive vs Traditional Drive Systems At a Glance
So, how do these systems really stack up against each other? This table breaks down the fundamental differences at a high level, making it clear where each one shines (or doesn't).
| Attribute | Direct Drive System | Geared System | Belt-Driven System |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Complexity | Very Low | High | Moderate |
| Efficiency | Very High (95%+) | Moderate (70-90%) | Good (85-95%) |
| Precision & Accuracy | Excellent (No backlash) | Good (Has backlash) | Fair (Belt stretch/slip) |
| Maintenance | Minimal | High (Lubrication, wear) | Moderate (Tensioning, replacement) |
| Speed/Torque | High torque, low speed | High torque, variable speed | Flexible speed, lower torque |
| Acoustic Noise | Very Low | High | Low to Moderate |
| System Footprint | Compact | Bulky | Can be large |
As you can see, while traditional systems still have their place for certain applications, direct drive technology offers a clear advantage when precision, efficiency, and low maintenance are your top priorities.
How Direct Drive Actually Pays Off on the Production Floor
Knowing the theory behind a direct drive motor is one thing, but watching it transform a real-world production line is where the lightbulb really goes on. For plant engineers and system integrators, the appeal goes way beyond the specs. We're talking about real, measurable business outcomes—less scrap, smaller energy bills, and machines that just run.
Let's break down these advantages by looking at the common headaches they solve.
Unlocking a New Level of Precision and Quality
Think about a high-speed CNC machine grinding out intricate medical parts where tolerances are microscopically tight. With a classic geared system, you're always fighting backlash—that tiny bit of play between gear teeth. It might seem small, but it introduces positioning errors that lead directly to rejected parts, wasted material, and blown production costs.
Now, swap in a direct drive motor. By connecting the motor straight to the machine's lead screw, you eliminate all that mechanical slack. The system becomes incredibly stiff and responsive, turning every command from the controller into precise, repeatable motion. The result? A perfect surface finish, flawless part geometry, and a scrap rate that drops through the floor. This isn't just a minor improvement; it's how you build a competitive edge based on quality.
When you remove the mechanical middlemen—the gears, belts, and couplings that create backlash and compliance—a direct drive motor delivers a level of precision that's simply out of reach for traditional systems. This has a direct impact on product quality, cuts material waste, and boosts throughput.
This kind of precision is exactly why the technology is taking off. The direct drive rotary motor market is on a tear, projected to hit USD 8.444 billion by 2025. That growth is fueled by integrators and plant managers who need simpler motor controls and rock-solid reliability to hit their production goals. You can get a deeper look at the market trends for direct drive motors and see how they're driving efficiency across industries.
Slashing Energy Costs Where It Counts
Every facility manager has operational expenses in their crosshairs, and energy consumption is always a big target. Take a massive conveyor system in a distribution center running around the clock. A belt- or chain-driven setup is constantly bleeding energy through friction and mechanical loss. You can feel it as heat and hear it as noise, but on the balance sheet, it's just wasted money.
A direct drive motor completely rewrites that math. By getting rid of the transmission hardware, it can hit an efficiency rating of over 95%. That means almost every watt of electricity gets converted into useful work. For that same conveyor system, making the switch to direct drive can deliver a serious, measurable drop in kilowatt-hour usage, putting money back into the budget month after month.
Taking the Maintenance Burden Off Your Team
Picture a busy packaging line where a critical machine depends on a gearbox. The maintenance schedule is a constant grind of oil checks, lubrication, and planning for the next inevitable gearbox replacement. An unexpected failure brings everything to a halt, sending the maintenance team scrambling for hours while the line sits idle. That reactive fire-fighting drains resources and kills productivity.
A direct drive motor just erases those failure points. There’s no gearbox oil to change, no belts to tighten, and no chains to lube. The maintenance workload shrinks dramatically, freeing up your skilled techs to focus on proactive improvements instead of just patching things up. This doesn't just cut maintenance costs; it boosts your Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) by keeping the machines running. For any plant engineer, that’s the definition of a smoother, more predictable operation.
How to Select the Right Direct Drive Motor
Picking the right direct drive motor isn’t as simple as grabbing a standard NEMA-frame motor off the shelf. Because this component becomes a core part of your machine's structure—not just a bolt-on part—the selection process has to go much deeper. You're balancing raw performance, mechanical fit, and long-term reliability all at once.
Think of it less like choosing a motor and more like designing a custom powertrain. You wouldn't put a drag racing engine in a rock crawler, right? The same logic applies here. You need to intimately understand your load, your motion profile, and the physical space you have to work with. Get this right, and you unlock the incredible precision and power that direct drive offers.
Often, the whole decision boils down to a fundamental choice: are you chasing ultimate precision or maximum efficiency?
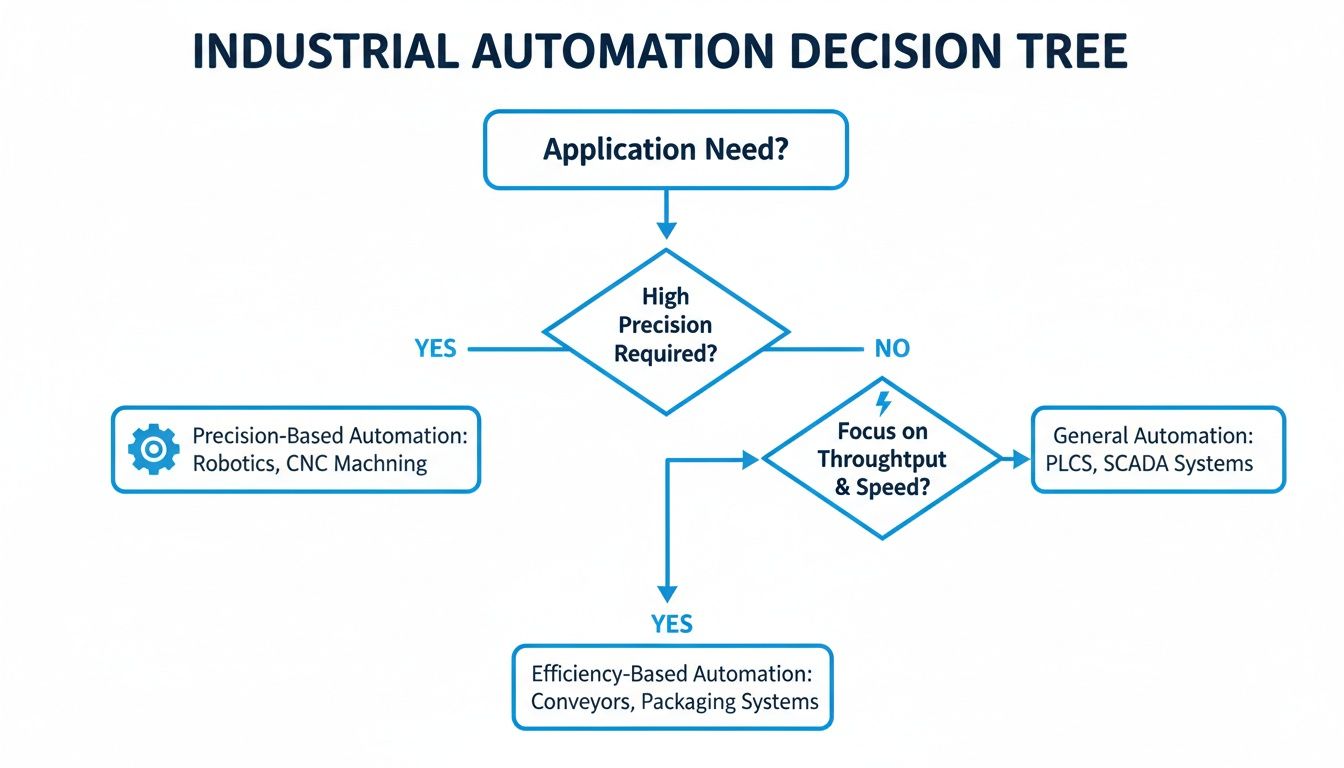
As you can see, there's a clear path. Your end goal—whether it's hitting a micron-level target or just slashing energy bills—will point you toward the best technology for the job.
Analyzing Your Torque Requirements
First thing's first: you absolutely have to nail down your torque requirements. Getting this wrong is probably the most common (and costly) mistake we see. In the world of direct drive, torque is a two-part story: continuous torque and peak torque.
Continuous Torque (RMS): This is the workhorse spec. It’s the average muscle the motor needs to flex during a normal cycle just to keep things moving against friction and gravity. This number is the biggest driver of the motor's physical size and how much heat it’s going to generate.
Peak Torque: Think of this as the motor’s adrenaline shot. It's the maximum force needed for those brief, intense moments of acceleration and deceleration. If you undersize for peak torque, you're asking for stalls and faults when the machine is pushed hardest.
You really need to map out your entire motion profile—the ramps up, the constant speed cruises, and the ramps down. It’s worth spending the time here. If you need a refresher, you can learn more about torque calculation for motors in our guide to make sure your calculations are rock solid.
Matching Motor and Load Inertia
Inertia—an object’s stubborn resistance to speeding up or slowing down—is a huge deal in high-performance servo systems. The key metric is the inertia ratio, which compares the inertia of your load to the inertia of the motor's rotor. A bad mismatch here is a recipe for disaster, leading to overshoot, ringing, and sloppy control.
A good rule of thumb for direct drive systems is to keep the load-to-motor inertia ratio below 10:1. While direct drive is inherently more stable than a geared system, staying in this ballpark is what gives the servo drive the authority it needs to keep the load under tight control for crisp, precise movements.
It’s like trying to steer a massive barge with a tiny outboard motor. The motor (the rudder) just doesn't have enough control over the barge's momentum (the load inertia). A low inertia ratio is like having a properly sized rudder—you get instant, predictable control.
Mechanical and Environmental Considerations
Beyond pure performance numbers, you have to think about how this motor will physically live inside your machine. This is where you get into the nitty-gritty of mounting, bearings, and making sure the motor doesn't cook itself.
Mounting and Form Factor
Direct drive motors generally come in two flavors, each with its own pros and cons:
- Frameless (Kit Motors): This is the pure, minimalist approach. You get a separate rotor and stator and design them right into your machine’s housing. It’s the ticket to the most compact and rigid setup possible, but it puts more of the engineering burden on you for alignment and bearing support.
- Housed Motors: These are much closer to a conventional motor—a self-contained unit with its own housing, bearings, and shaft. They are far simpler to bolt on and get running, but you sacrifice some of the design compactness you’d get with a frameless motor.
Bearing and Thermal Management
Remember, the motor is directly connected to the load. That means the motor's bearings are now responsible for supporting the full weight and operational forces of your payload. Always double-check that the motor’s specified axial and radial load ratings can handle what you’re throwing at them.
Finally, don’t forget about heat. A motor's continuous torque rating is entirely dependent on its ability to stay cool. Make sure your design has a plan for heat dissipation, whether it's simple convection, a fan, or even a liquid cooling loop for those really demanding, high-duty-cycle applications. Overheating is a surefire way to kill a motor’s performance and shorten its life.
Integrating Motors with Your Control Systems
A high-performance direct drive motor is only half the story. You can have the best motor in the world, but its real power is only unleashed when you pair it with the right control system. The relationship between the motor and its servo drive or Variable Frequency Drive (VFD) is everything—it’s the brain and central nervous system of your entire machine.
Getting this pairing right is what separates a world-class machine from a constant headache. It’s all about matching the right components, fine-tuning the software, and making sure everything talks to each other flawlessly to execute perfect motion, every single time.
Choosing the Right Feedback Device
Before a control system can tell a motor what to do, it needs to know exactly where the motor is. That’s the job of the feedback device, which acts as the system's eyes and ears. The two most common options are encoders and resolvers, and your choice really boils down to your application's environment and how much precision you need.
- Encoders: These are your high-resolution digital specialists. If you need extreme accuracy for something like CNC machining or semiconductor manufacturing, an encoder is the way to go. They deliver incredible precision but can be a bit sensitive to tough conditions like heavy vibration or contamination.
- Resolvers: Think of resolvers as the rugged old pros of feedback. They're analog devices that are built like a tank, capable of handling extreme temperatures, shock, and dirty environments without breaking a sweat. While they might not have the razor-sharp resolution of a high-end encoder, their sheer durability makes them the go-to choice for heavy-duty jobs like stamping presses or steel mills.
It's that classic trade-off: precision versus toughness. You have to take a hard look at where the machine will live and operate to make sure the feedback device will keep sending reliable data for years.
The Art of Servo System Tuning
Once you've physically connected the motor and feedback device to the drive, the real magic begins. This is where tuning comes in. It’s the process of adjusting the control loops—usually the proportional, integral, and derivative (PID) gains—inside the drive so the motor’s response perfectly matches the load it’s moving.
Think of it like setting up the suspension on a race car for a specific track. A poorly tuned system will feel sloppy and out of control, causing the machine to overshoot its target, oscillate, or just feel sluggish. But when you nail the tuning, the machine becomes crisp, accurate, and incredibly stable. It settles into position instantly with zero wasted motion. This step is absolutely critical if you want to get every last bit of dynamic performance out of your direct drive motor.
A well-tuned servo system is the cornerstone of high-performance automation. It ensures the machine responds instantly and accurately to commands, directly impacting product quality, throughput, and operational efficiency. Neglecting this step means leaving significant performance on the table.
Ensuring Seamless Communication and Safety
Your direct drive motor and its controller don't work in a bubble. They need to communicate with the rest of your automation system, like the Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) running the show and the Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) operators use. This demands a solid communication protocol, like EtherNet/IP or PROFINET, to keep real-time data flowing. For a deeper dive into how drives fit into the big picture, our guide on the role of a motor variable speed controller in modern systems is a great resource.
But the most important piece holding all this together is the UL-listed control panel. This isn't just a metal box to stick your components in; it’s an engineered safety system that ensures everything is wired correctly, protected from faults, and compliant with national safety standards. A well-designed, custom-built panel provides reliable power distribution, overcurrent protection, and a safe operating environment.
Honestly, working with a single integrator who can deliver the whole package—the motor, the drive, and the certified UL-listed panel—is a game-changer. It gets rid of the finger-pointing that happens when you source parts from different vendors. You get a complete system that’s designed, built, and tested to work together from day one, which helps you sidestep those costly integration nightmares and project delays that can completely derail a production schedule. It’s a holistic approach that guarantees safety, compliance, and rock-solid reliability.
Getting Installation and Troubleshooting Right
A direct drive motor is only as good as its installation. Period. Unlike a forgiving belt or chain system that can mask minor imperfections, a direct connection demands precision. Getting the installation right isn't just about making the machine run—it's the bedrock of long-term reliability and your first line of defense against premature, costly failures.
Think of it like building a house. A slightly off-kilter foundation creates huge problems for the framers, the roofers, and everyone else down the line. It's the same with a direct drive motor; nail the alignment and mounting, and you're setting it up for a long, smooth operational life.
This is the field-level advice you need—from proactive installation steps to reactive troubleshooting—to keep your equipment humming and maximize uptime.
Critical Installation Checklist
Your best weapon against future downtime is meticulous attention during the initial setup. A few thousandths of an inch of misalignment might not seem like much, but it's enough to introduce killer stresses that will chew up bearings and cause vibration issues.
Stick to this checklist for a flawless installation:
- Verify Mounting Surfaces: Before you even think about lifting the motor, get down and inspect the mounting surfaces. Are they perfectly flat, rigid, and clean? Any burrs, old gasket material, or unevenness will create a stress point the second you tighten the bolts.
- Nail the Alignment: Break out the precision tools—laser alignment systems, dial indicators, whatever it takes. The motor shaft and the driven load have to be perfectly concentric and parallel. This is the single most important step for preventing premature bearing wear.
- Secure All Fasteners: Don't just "get 'em tight." Use a calibrated torque wrench and tighten every mounting bolt to the manufacturer's exact spec. If they recommend a thread-locking compound, use it. Vibration has a knack for loosening things you thought were secure.
- Confirm Electrical Connections: Go through all power, feedback, and communication wiring twice. Connections must be tight, shielded from electrical noise (keep them away from high-voltage lines!), and properly terminated. A loose wire is one of the most common culprits behind erratic motor behavior.
Troubleshooting Common Failure Modes
Even a textbook installation can't prevent every issue. The key is knowing what to look for so you can diagnose problems fast and minimize disruption. When a direct drive motor starts acting up, it usually gives you clues.
A sudden spike in temperature or a new vibration is your machine's early warning system. Jump on those symptoms immediately. It’s a lot easier than dealing with a catastrophic failure that shuts down the entire line.
Here are the most common headaches and what's likely causing them.
Issue 1: Excessive Heat or Overheating
A hot motor is a stressed motor. It's often the first red flag signaling a deeper mechanical or electrical problem.
- Likely Causes:
- Mechanical Binding: The load is fighting back. Something is causing more friction than expected, maybe from misalignment or a problem in the driven components.
- Incorrect Drive Parameters: Check the servo drive settings. If the current limit or tuning gains are cranked too high, you're essentially forcing the motor to body-slam the load on every move.
- Insufficient Cooling: Are the vents blocked? Is the cabinet fan working? Heat has to go somewhere, and if it can't escape, it will cook the motor. Good protection of motors always starts with smart thermal management.
Issue 2: Unwanted Vibration or Noise
A healthy direct drive system is smooth and quiet. If you hear or feel a new vibration, it’s time to investigate.
- Likely Causes:
- Mechanical Imbalance: The problem might not be the motor but the load it's attached to. An unbalanced load creates a cyclical vibration that gets worse with speed.
- Loose Components: Go back and check every single mounting bolt and coupling. You'd be surprised how much noise a single loose fastener can make.
- Servo Tuning Instability: If the drive's PID loops are poorly tuned, the motor can start to oscillate or "hum" as it fights itself to hold a position. This is often a software fix—a quick re-tune can solve it.
Issue 3: Positioning Errors or Inaccuracy
The motor isn't hitting its marks, overshooting the target, or seems to be off by a consistent amount. The issue is almost always in the control loop.
- Likely Causes:
- Feedback Device Issues: The drive is flying blind. A loose encoder, a nicked cable, or electrical noise scrambling the signal can corrupt the position data the drive relies on.
- Mechanical Backlash (in the load): The motor itself has zero backlash, but that doesn't mean the rest of your machine doesn't. Check downstream couplings, gearheads, or actuators for any slop.
- Incorrect Tuning: A sluggish or overly aggressive tuning profile will cause consistent positioning errors. The system is either too slow to react or too jumpy to settle accurately.
Your Direct Drive Motor Questions, Answered
Jumping into any new technology brings up questions. It's only natural. For OEMs, plant engineers, and anyone looking to boost machine performance, getting the right answers about direct drive motors is the first step toward a successful project.
Let's cut through the noise and tackle the most common questions we hear from the field.
Are Direct Drive Motors Really More Expensive Than Geared Systems?
This is always question number one, and for good reason. If you just look at the upfront price tag, a direct drive motor can seem more expensive than a standard motor and gearbox combo. But that’s only a tiny piece of the puzzle.
You have to look at the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO). A direct drive system completely gets rid of gearboxes, couplings, belts, and pulleys. That’s a shorter bill of materials right there, not to mention less inventory to manage.
The real savings, though, come over the life of the machine. Think about it: no more worn-out gears, no more stretched belts, and no more scheduled lubrication. Maintenance costs plummet. Add in their incredible energy efficiency—often over 95%—and you’ll see the difference on your electricity bill.
When you can't afford a single minute of downtime and precision is everything, the math almost always works out. The reduced maintenance and energy savings mean a direct drive motor pays for itself, delivering a much lower TCO and a faster return on your investment.
Where Do Direct Drive Motors Make the Most Sense?
Direct drive motors are absolute game-changers in applications where precision, speed, and rock-solid reliability are make-or-break. They shine wherever the mechanical "slop" and backlash from a traditional transmission system is causing quality problems or limiting how fast you can run.
We see them deliver huge results in places like:
- CNC Machining: To get those flawless surface finishes and hold incredibly tight tolerances that backlash makes impossible.
- Robotics: For precise, repeatable movements, cycle after cycle, without the positioning errors that pop up as gears wear down.
- High-Speed Packaging and Sorting: To keep products moving quickly and ensure everything lands exactly where it needs to, every time.
- Indexing Tables and Turrets: For lightning-fast, accurate positioning in automated assembly lines.
Bottom line? If your machine suffers from the wear, tear, and maintenance headaches of a traditional gearbox or belt drive, it's a prime candidate for a direct drive upgrade. They are especially powerful in automated systems where tweaking a gearbox is a nightmare and downtime costs a fortune.
How Do I Size a Direct Drive Motor Correctly?
This is where the engineering really comes in. Sizing a direct drive motor isn't like picking a standard motor off the shelf; it requires a deep dive into your application's specific motion profile. Getting this right is absolutely critical.
You have to nail down a few key parameters:
- Peak Torque: What's the absolute maximum torque you need for the toughest part of the job, usually the acceleration and deceleration phases?
- Continuous (RMS) Torque: What's the average torque needed to keep things running smoothly and overcome friction throughout the entire work cycle?
- Load Inertia: This is a big one. The ratio of the load's inertia to the motor's rotor inertia is crucial for stable control. A load-to-motor inertia ratio under 10:1 is a good target to shoot for.
- Maximum Speed: How fast does this thing really need to go?
- Mechanical Constraints: You have to consider the physical space you have to work with and make sure the motor’s bearings can handle the unique axial and radial loads of your machine.
Because there are so many variables, it's a smart move to work with an experienced integrator. An expert can run the numbers, analyze your machine's dynamics, and help you select the perfect motor and drive combination for the job.
Can I Swap Out My Old Geared Motor for a Direct Drive?
Absolutely. Retrofitting an existing machine with a direct drive motor is a fantastic way to breathe new life into it and unlock more performance. But it's rarely a simple drop-in replacement.
First, you'll have to tackle the mechanical side by designing a new mounting solution to connect the motor directly to your load, ensuring perfect alignment. Electrically, you’ll definitely need a new servo drive that's properly matched to the motor. And finally, your control system will need to be re-tuned to take full advantage of the motor's incredibly fast response and stiffness.
It's an engineering project, no doubt about it. But the payoff in precision, energy savings, and massively reduced maintenance often makes it one of the best investments you can make in your equipment.
At E & I Sales, we don't just sell parts; we engineer complete solutions. From sizing and selecting the right motor to designing and building custom UL-listed control panels, our team is your single source for making sure your direct drive system performs flawlessly from day one. https://eandisales.com

